Month-end close: Best practice
The month-end close is one of the most frequent and important accounting processes. It ensures that all financial activity is complete, accurate, categorized correctly, reconciled, and any discrepancies resolved. This process is critical to maintain reliable and audit-ready data.
Use Cryptio’s Needs Review tabs and reports to complete the month-end close. This checklist provides a high-level guide.
Step 1: Data Completeness
Verify all sources are imported.
Make sure all wallets, exchanges, and custody accounts are connected in your workspace. Missing sources create incomplete reconciliations and unreliable data.
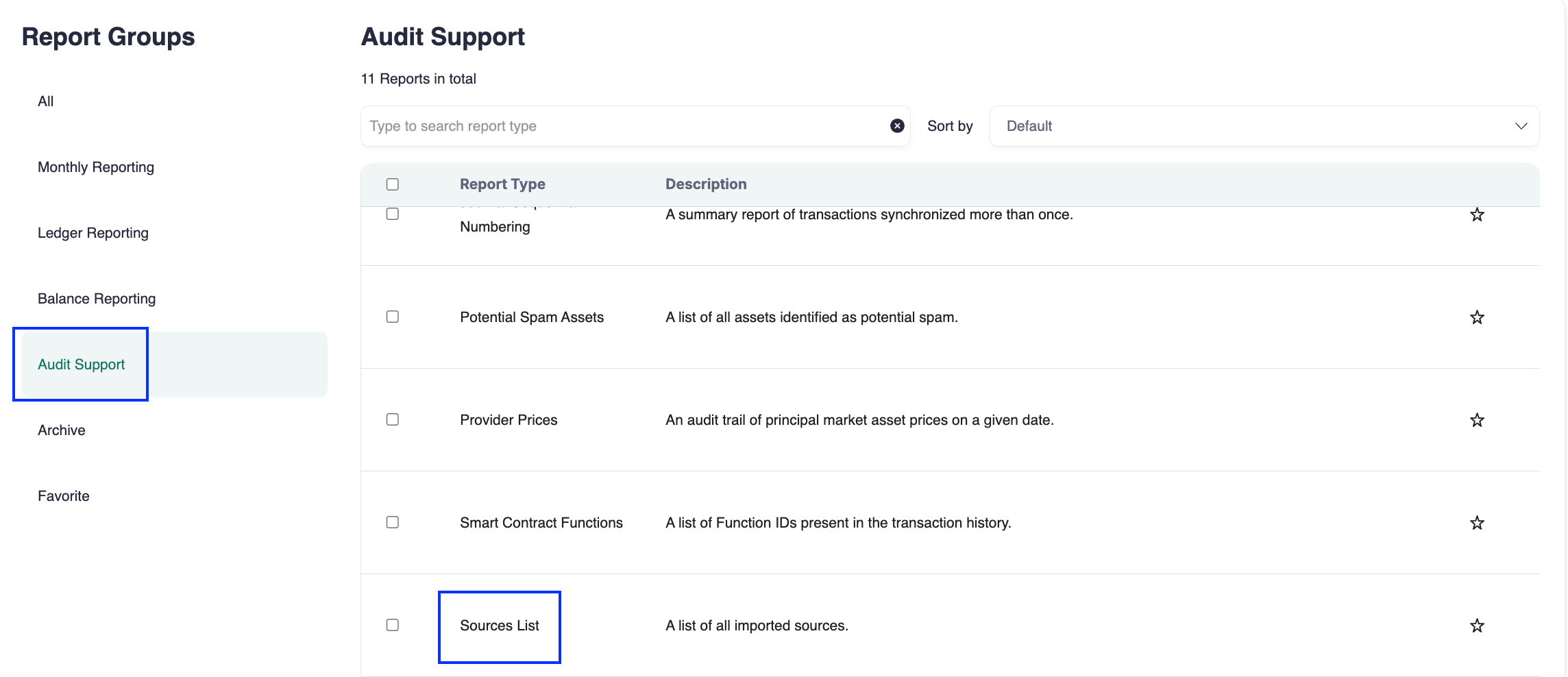
Run the Source List report to check for asset changes between periods.
Keep an internal list of all income sources and note the date each was added. Compare this list with your Cryptio workspace monthly.
Update internal transfer and vendor contacts.
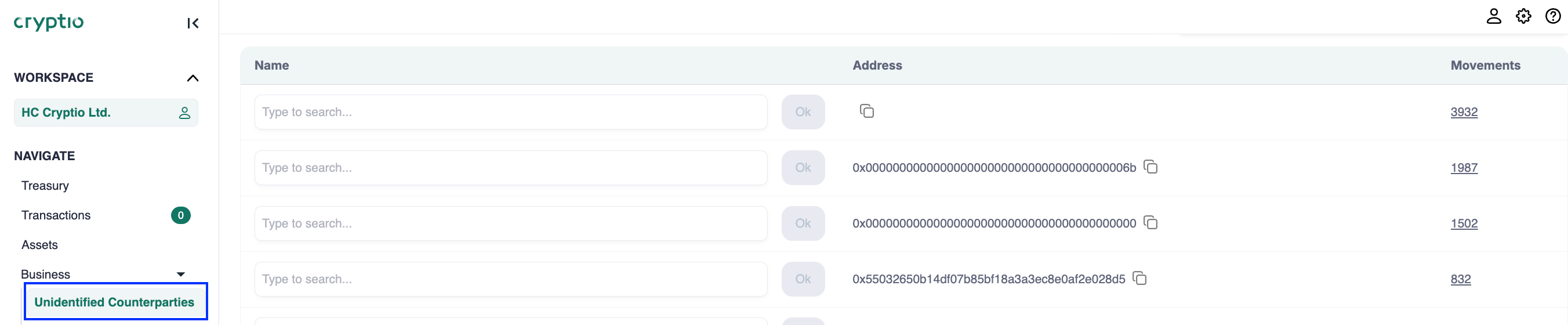
Not all movements are disposals. Disposals can result in gains or losses, while some events (like internal transfers) are non-disposals. To avoid overstating gains, mark all company-controlled addresses as internal in Cryptio.
Go to Business > Unidentified Counterparties to label addresses with recognizable names.
Maintain an internal list of all controlled addresses and reconcile it monthly against Cryptio’s list.
Step 2: Data Accuracy
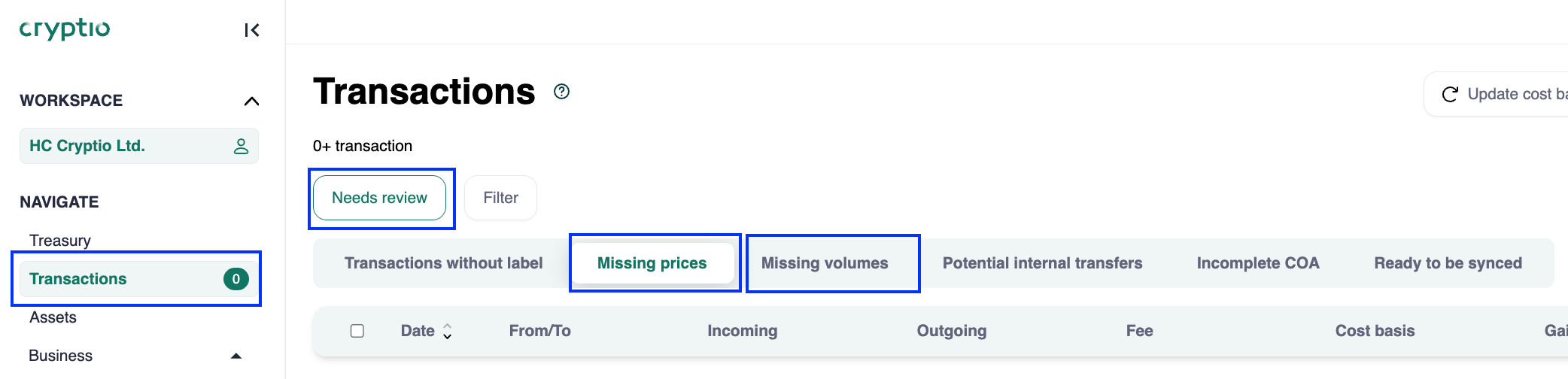
Resolve missing prices or volumes.
These issues usually arise when standard pricing methods can’t be applied. Missing values prevent syncing to ERP.
Go to Transactions > Needs review, then check the Missing prices and Missing volumes tabs.
To reduce pressure at month-end, review missing data weekly instead of waiting until close.
Investigate discrepancies.
Compare balances across systems (e.g., Coinbase vs. Cryptio).
Reconcile balances using asset roll-forwards or dashboards under the Treasury module.
Step 3: CoA Accuracy
Review categorization and labels.
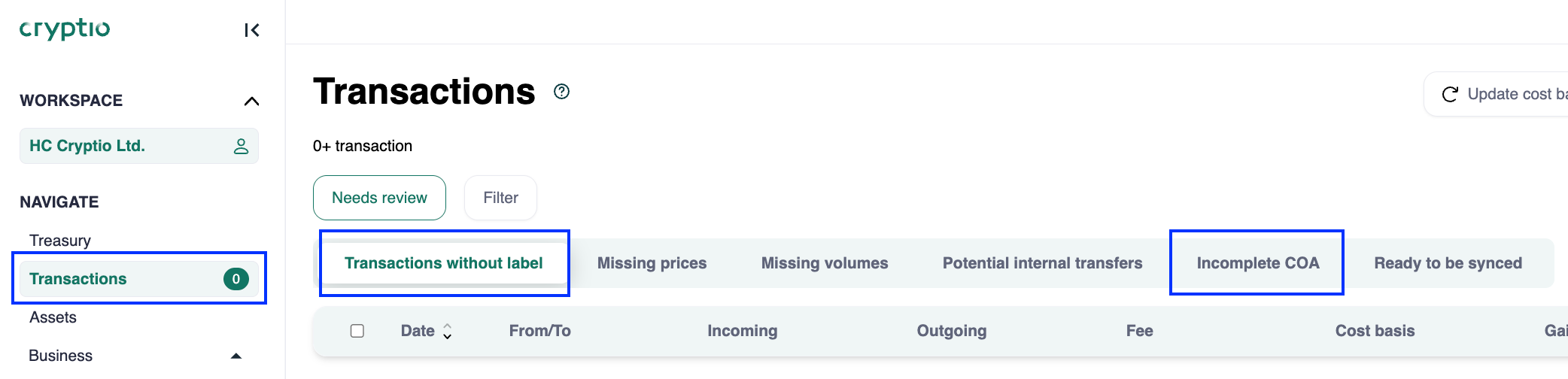
Go to Transactions > Needs review > Transactions without label to find unlabelled transactions.
Confirm Chart of Accounts mapping.
Each transaction should be mapped to an account type: Assets, Liabilities, Equity, Revenue, or Expenses.
Go to Transactions > Needs review > Incomplete CoA to find missing mappings.
Use consistent account numbering for structure. Example ranges:
Assets: 10000–19999
Liabilities: 20000–29999
Equity: 30000–39999
Revenue: 40000–49999
Expenses: 50000–59999
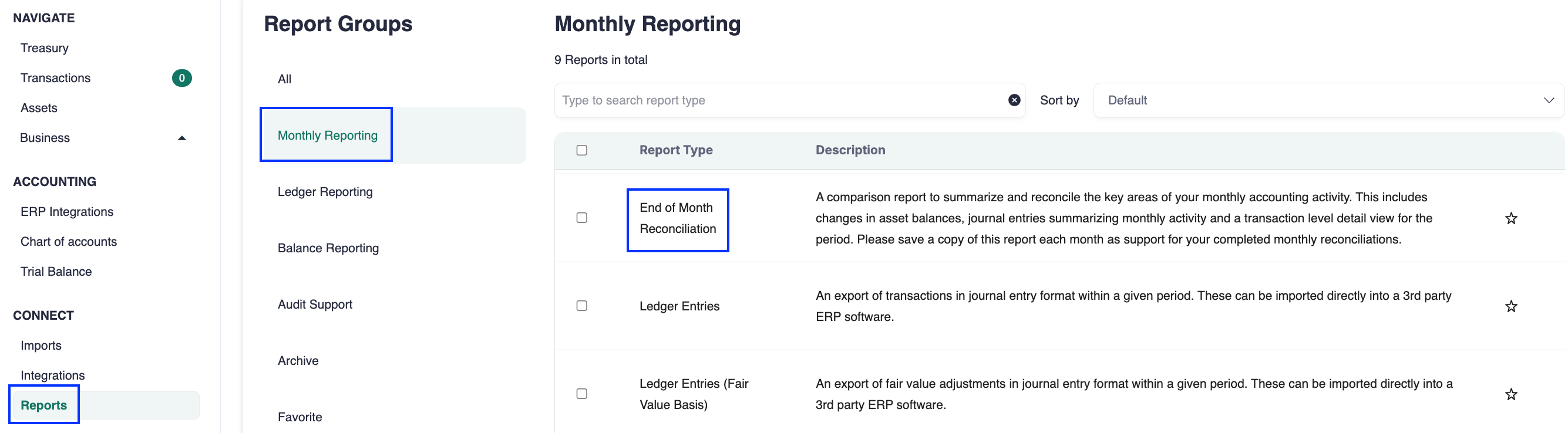
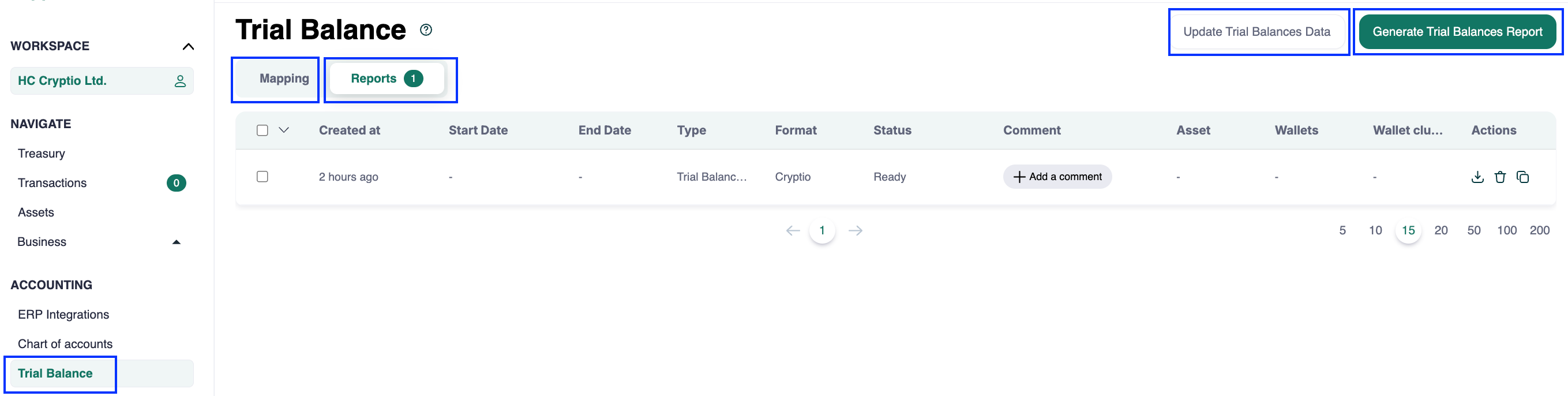
Step 4: Generate the End-of-Month Reconciliation Report
This report consolidates everything you need: Ledger entries, asset roll-forward, trial balance, and transaction history.
Check that:
Asset roll-forwards match all transactions for the period.
Ledger entries align with the transactions you want to sync into ERP.
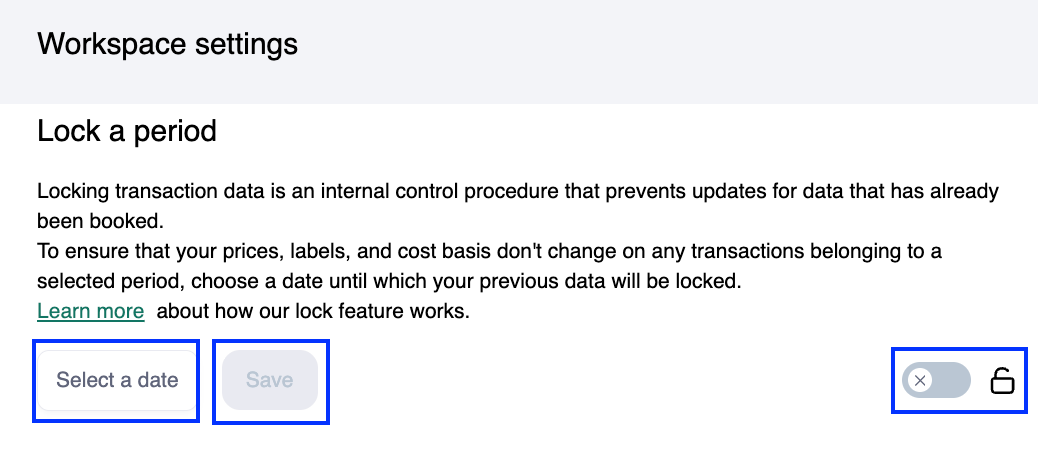
Step 5: Period Locking and Impairment (if applicable)
Use Cryptio’s Locking Data feature to prevent changes to closed periods.
If you are under US GAAP and in-scope for ASC 350-60, use the FMV adjustment instead of impairment.
For some users, the Impairment module can generate updated balances and impairment reports.
How to decide:
Are you US GAAP and in-scope for ASC 350-60?
→ Yes: Use FMV adjustment.
→ No: Follow impairment guidance.
Step 6: Sync to ERP
Prepare journal entries that summarize reconciled activity.
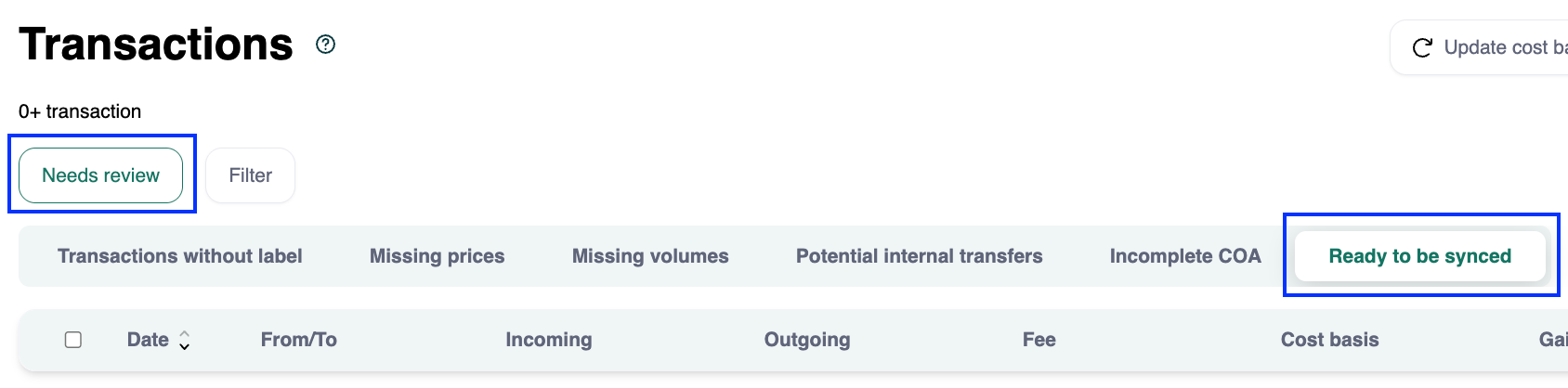
Go to Transactions > Needs review > Ready to be synced to review transactions.
Push them as journal entries to your ERP.
For non-ERP users, generate the Ledger entries report instead.
Step 7: Compare ERP Data with Cryptio Data
Reconcile sub-ledgers and trial balance by comparing account balances.
Use the trial balance from the reconciliation report to complete this check.
Step 8: Save Documentation
Generate financial reports (trial balance, income statement, cash flow statement) for management review.
Store these as part of your month-end close package for audit readiness.
Best Practice Reminder
Completeness and accuracy are both essential. While Step 2 focuses on data accuracy, remember that completeness must be confirmed first (Step 1) or accuracy checks won’t be reliable.